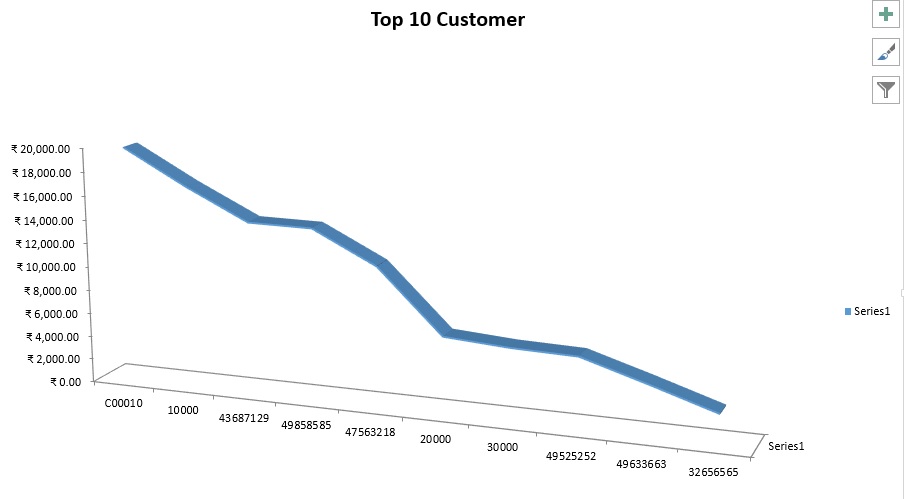
This example shows how to handle enumerations by creating a graph in Excel that shows the distribution of Sales by Customer.
You will run the codeunit directly from Object Designer. In a real application, you would call it from an appropriate place, such as from a menu or any other window.
About This Walkthrough
This walkthrough illustrates the following tasks:
- Creating a codeunit that declares the Automation variables that are required for using Excel Automation.
- Adding a function to calculate Top 10 Customers Sales Contribution.
- Adding C/AL code to the codeunit to run the Automation object that opens Excel.
- Adding C/AL code to the Automation codeunit to transfer data from a table record to Excel.
- Adding C/AL code that creates a graph in Excel.
Prerequisites
To complete this walkthrough, you will need:
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2015 with a developer license.
- The CRONUS International Ltd. demo data company.
- Microsoft Excel 2013 or Microsoft Excel 2010.
Creating the Codeunit and Declaring Variables
To create the codeunit and declare variables
- To implement Automation in a codeunit, you define the Automation variables. To define an Automation variable, you specify an Automation server and the Automation object.
- The language in the regional settings of your computer matches the language version of Microsoft Excel.
- In Object Designer, choose Codeunit, and then choose the New button to create a new codeunit.
- On the View menu, choose C/AL Globals.
- On the Variables tab, add the following variables:
Note
For the Automation data type variables, the subtype Microsoft Excel 15.0/14.0 Object Library defines the Automation server, and the class specifies the Automation object of the Microsoft Excel 15.0/14.0 Object Library.
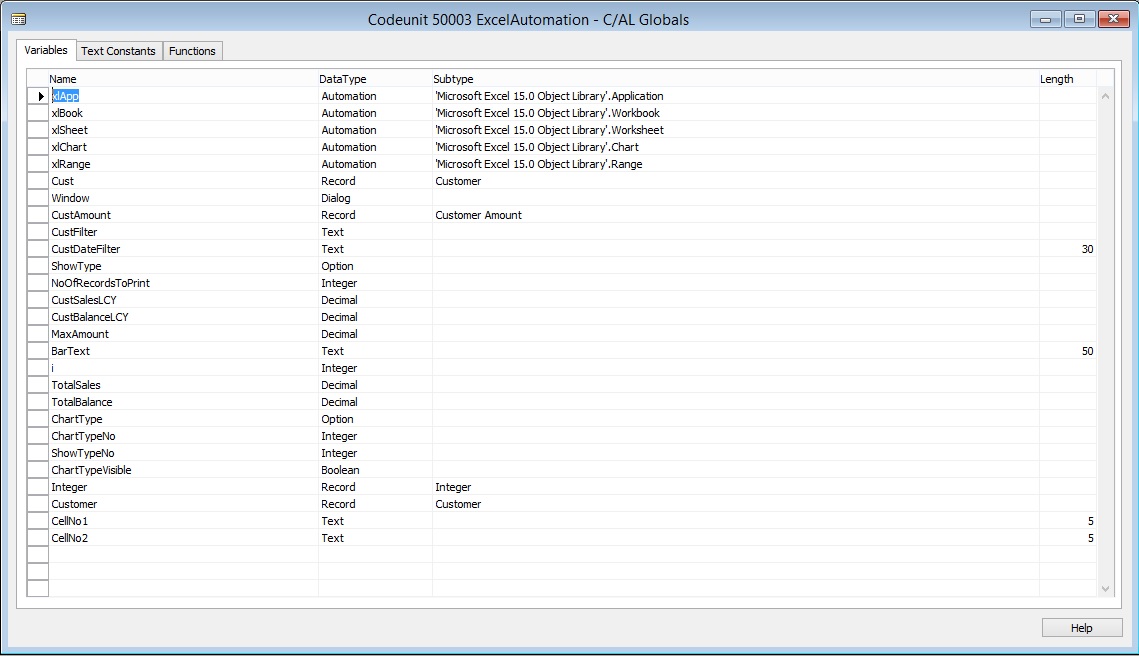
| Name | DataType | Subtype | Length |
| xlApp | Automation | 'Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library'.Application | |
| xlBook | Automation | 'Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library'.Workbook | |
| xlSheet | Automation | 'Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library'.Worksheet | |
| xlChart | Automation | 'Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library'.Chart | |
| xlRange | Automation | 'Microsoft Excel 15.0 Object Library'.Range | |
| Cust | Record | Customer | |
| Window | Dialog | ||
| CustAmount | Record | Customer Amount | |
| CustFilter | Text | ||
| CustDateFilter | Text | 30 | |
| ShowType | Option | [Sales (LCY),Balance (LCY)] | |
| NoOfRecordsToPrint | Integer | ||
| CustSalesLCY | Decimal | ||
| CustBalanceLCY | Decimal | ||
| MaxAmount | Decimal | ||
| BarText | Text | 50 | |
| i | Integer | ||
| TotalSales | Decimal | ||
| TotalBalance | Decimal | ||
| ChartType | Option | [Bar chart,Pie chart] | |
| ChartTypeNo | Integer | ||
| ShowTypeNo | Integer | ||
| ChartTypeVisible | Boolean | ||
| Integer | Record | Integer | |
| Customer | Record | Customer | |
| CellNo1 | Text | 5 | |
| CellNo2 | Text | 5 |
- Close the C/AL Globals window.
Adding the Code
Now you add the code for the codeunit.
To add the code
- Add a Function to calculate Top 10 Customers Sales Contribution as:

Add code to it as:
I have not used all the values, just shown this way also you can think of while you design any such code & functions.
Window.OPEN(Text000);
i := 0;
Cust.RESET;
IF Cust.FINDSET THEN
REPEAT
Window.UPDATE(1,Cust."No.");
Cust.CALCFIELDS("Sales (LCY)","Balance (LCY)");
IF (Cust."Sales (LCY)" <> 0) OR (Cust."Balance (LCY)" <> 0) THEN
BEGIN
CustAmount.INIT;
CustAmount."Customer No." := Cust."No.";
IF ShowType = ShowType::"Sales (LCY)" THEN BEGIN
CustAmount."Amount (LCY)" := -Cust."Sales (LCY)";
CustAmount."Amount 2 (LCY)" := -Cust."Balance (LCY)";
END ELSE BEGIN
CustAmount."Amount (LCY)" := -Cust."Balance (LCY)";
CustAmount."Amount 2 (LCY)" := -Cust."Sales (LCY)";
END;
CustAmount.INSERT;
IF (NoOfRecordsToPrint = 0) OR (i < NoOfRecordsToPrint) THEN
i := i + 1
ELSE BEGIN
CustAmount.FIND('+');
CustAmount.DELETE;
END;
TotalSales += Cust."Sales (LCY)";
TotalBalance += Cust."Balance (LCY)";
ChartTypeNo := ChartType;
ShowTypeNo := ShowType;
END;
UNTIL Cust.NEXT = 0;
CustSalesLCY := Cust."Sales (LCY)";
CustBalanceLCY := Cust."Balance (LCY)";
Window.CLOSE;
IF CustAmount.FIND('-') THEN
REPEAT
CustAmount."Amount (LCY)" := -CustAmount."Amount (LCY)";
Customer.GET(CustAmount."Customer No.");
Customer.CALCFIELDS("Sales (LCY)","Balance (LCY)");
IF MaxAmount = 0 THEN
MaxAmount := CustAmount."Amount (LCY)";
CustAmount."Amount (LCY)" := -CustAmount."Amount (LCY)";
UNTIL CustAmount.NEXT = 0;
- In the C/AL Editor, make call to above function by adding the following code to the OnRun trigger.
CustAmount.DELETEALL;
TopTenCustomer(10,ShowType::"Sales (LCY)",ChartType::"Bar chart");
- Create an instance of Excel by adding the following code.
CREATE(xlApp, FALSE, TRUE);
- Add a new workbook to Excel.
xlBook := xlApp.Workbooks.Add(-4167);
xlSheet:= xlApp.ActiveSheet;
xlSheet.Name := ‘Top 10 Customer';
The following describes the code:
- In the first line, you use the Add method of the Workbooks collection to return a new workbook. The attribute -4167 is the enumerator value of worksheets as they apply to Workbook objects.
- In the second line, you use the ActiveSheet property of the Application class to ensure that what is done next affects the active sheet of the new workbook.
- In the third line, you use the Name property to name the sheet.
Transferring Data
To transfer the data, you must calculate the data and transfer the results of the calculation.
To transfer data
- In the C/AL Editor, on the codeunit, use following code to transfer data of Top 10 Customers to Excel. To transfer the data to Microsoft Excel, add the following code.
CellNo1 := 'A1';
CellNo2 := 'B1';
IF CustAmount.FINDSET THEN
REPEAT
CellNo1 := INCSTR(CellNo1);
xlSheet.Range(CellNo1).Value := CustAmount."Customer No.";
CellNo2 := INCSTR(CellNo2);
xlSheet.Range(CellNo2).Value := ABS(CustAmount."Amount (LCY)");
UNTIL CustAmount.NEXT = 0;
- The final step is to create the graph. You will use the ChartWizard method to create chart. This is a fast and simple way to do it. You can more tightly control the design of the graph by setting it up using the methods and properties of the various Chart objects, such as ChartArea and Legend.
Creating the Graph
The final step is to create the graph. You will use the ChartWizard method to create chart. This is a fast and simple way to do it. You can more tightly control the design of the graph by setting it up using the methods and properties of the various Chart objects, such as ChartArea and Legend.
To create the graph
- In the C/AL Editor, on the current codeunit, define a range for the data in the graph.
xlRange := xlSheet.Range('A2:'+FORMAT(CellNo2));
- Add a new chart sheet and give it a name.xlChart.Name := ' Top 10 Customer - Graph';
xlChart := xlBook.Charts.Add;
xlChart.Name := ' Top 10 Customer - Graph';
- Create the graph.
xlChart.ChartWizard(xlRange,-4101,7,2,1,0,1,'Top 10 Customer');
The following table describes the optional arguments that are used in the ChartWizard method.
| Argument | Description | Value in method call |
| Source | The range that contains the source data for the new chart. | xlRange – The object returned by xlSheet.Range(‘A2:C3’). |
| Gallery | The chart type. | -4101 – The enumerator for the Chart Shown above. |
| Format | The option number for the built-in auto formats. | 7 |
| PlotBy | An integer specifying whether the data for each series is in rows or columns. | 2 – The enumerator for the xlRows XlRowCol enumerator. |
| CategoryLabels | An integer specifying the number of rows or columns within the source range that contains category labels. | 1 – There is one row with category labels (the department names). |
| SeriesLabels | An integer specifying the number of rows or columns within the source range that contains series labels. | 0 – There are no series labels in your data. |
| HasLegend | TRUE to include a legend. | 1 |
| Title | VARIANT with the title of the chart. | You pass a string such as ‘Top 10 Customer’. |
- Make Excel visible by adding the following code.
xlApp.Visible := TRUE;
Excel produces a General Protection Fault error when you close a new Excel worksheet that is created when Excel is invisible. To resolve this, you can make Excel visible immediately after you create a new worksheet. You can also make Excel visible just before you create a new Excel worksheet and then make it invisible again immediately after creating the new Excel worksheet. In this case, you would add the following code.
xlApp.Visible := TRUE;
xlBook := xlApp.Workbooks.Open(FileName);
xlApp.Visible := FALSE;
- Clearing the Temp Table by adding the following code.
CustAmount.DELETEALL;
- Complete code in OnRun trigger should look like below:

Saving and Running the Codeunit
You can test the codeunit for creating the graph by running the codeunit from Object Designer.
To save and run a codeunit
- On the File menu, choose Save.
- In the Save As window, enter an ID and name, and then choose the OK
- In Object Designer, select the codeunit, and then choose the Run
The Microsoft Excel graph should appear. As show above in beginning of the post.
Note
If you get an error states Old format or invalid type library, then make sure that the language in the regional settings of your computer matches the language version of Microsoft Excel.
Below detailed reference to the values used in above code:
XlChartType
| Name | Value | Description |
| xl3DArea | -4098 | 3D Area. |
| xl3DAreaStacked | 78 | 3D Stacked Area. |
| xl3DAreaStacked100 | 79 | 100% Stacked Area. |
| xl3DBarClustered | 60 | 3D Clustered Bar. |
| xl3DBarStacked | 61 | 3D Stacked Bar. |
| xl3DBarStacked100 | 62 | 3D 100% Stacked Bar. |
| xl3DColumn | -4100 | 3D Column. |
| xl3DColumnClustered | 54 | 3D Clustered Column. |
| xl3DColumnStacked | 55 | 3D Stacked Column. |
| xl3DColumnStacked100 | 56 | 3D 100% Stacked Column. |
| xl3DLine | -4101 | 3D Line. |
| xl3DPie | -4102 | 3D Pie. |
| xl3DPieExploded | 70 | Exploded 3D Pie. |
| xlArea | 1 | Area |
| xlAreaStacked | 76 | Stacked Area. |
| xlAreaStacked100 | 77 | 100% Stacked Area. |
| xlBarClustered | 57 | Clustered Bar. |
| xlBarOfPie | 71 | Bar of Pie. |
| xlBarStacked | 58 | Stacked Bar. |
| xlBarStacked100 | 59 | 100% Stacked Bar. |
| xlBubble | 15 | Bubble. |
| xlBubble3DEffect | 87 | Bubble with 3D effects. |
| xlColumnClustered | 51 | Clustered Column. |
| xlColumnStacked | 52 | Stacked Column. |
| xlColumnStacked100 | 53 | 100% Stacked Column. |
| xlConeBarClustered | 102 | Clustered Cone Bar. |
| xlConeBarStacked | 103 | Stacked Cone Bar. |
| xlConeBarStacked100 | 104 | 100% Stacked Cone Bar. |
| xlConeCol | 105 | 3D Cone Column. |
| xlConeColClustered | 99 | Clustered Cone Column. |
| xlConeColStacked | 100 | Stacked Cone Column. |
| xlConeColStacked100 | 101 | 100% Stacked Cone Column. |
| xlCylinderBarClustered | 95 | Clustered Cylinder Bar. |
| xlCylinderBarStacked | 96 | Stacked Cylinder Bar. |
| xlCylinderBarStacked100 | 97 | 100% Stacked Cylinder Bar. |
| xlCylinderCol | 98 | 3D Cylinder Column. |
| xlCylinderColClustered | 92 | Clustered Cone Column. |
| xlCylinderColStacked | 93 | Stacked Cone Column. |
| xlCylinderColStacked100 | 94 | 100% Stacked Cylinder Column. |
| xlDoughnut | -4120 | Doughnut. |
| xlDoughnutExploded | 80 | Exploded Doughnut. |
| xlLine | 4 | Line. |
| xlLineMarkers | 65 | Line with Markers. |
| xlLineMarkersStacked | 66 | Stacked Line with Markers. |
| xlLineMarkersStacked100 | 67 | 100% Stacked Line with Markers. |
| xlLineStacked | 63 | Stacked Line. |
| xlLineStacked100 | 64 | 100% Stacked Line. |
| xlPie | 5 | Pie. |
| xlPieExploded | 69 | Exploded Pie. |
| xlPieOfPie | 68 | Pie of Pie. |
| xlPyramidBarClustered | 109 | Clustered Pyramid Bar. |
| xlPyramidBarStacked | 110 | Stacked Pyramid Bar. |
| xlPyramidBarStacked100 | 111 | 100% Stacked Pyramid Bar. |
| xlPyramidCol | 112 | 3D Pyramid Column. |
| xlPyramidColClustered | 106 | Clustered Pyramid Column. |
| xlPyramidColStacked | 107 | Stacked Pyramid Column. |
| xlPyramidColStacked100 | 108 | 100% Stacked Pyramid Column. |
| xlRadar | -4151 | Radar. |
| xlRadarFilled | 82 | Filled Radar. |
| xlRadarMarkers | 81 | Radar with Data Markers. |
| xlStockHLC | 88 | High-Low-Close. |
| xlStockOHLC | 89 | Open-High-Low-Close. |
| xlStockVHLC | 90 | Volume-High-Low-Close. |
| xlStockVOHLC | 91 | Volume-Open-High-Low-Close. |
| xlSurface | 83 | 3D Surface. |
| xlSurfaceTopView | 85 | Surface (Top View). |
| xlSurfaceTopViewWireframe | 86 | Surface (Top View wireframe). |
| xlSurfaceWireframe | 84 | 3D Surface (wireframe). |
| xlXYScatter | -4169 | Scatter. |
| xlXYScatterLines | 74 | Scatter with Lines. |
| xlXYScatterLinesNoMarkers | 75 | Scatter with Lines and No Data Markers. |
| xlXYScatterSmooth | 72 | Scatter with Smoothed Lines. |
| xlXYScatterSmoothNoMarkers | 73 | Scatter with Smoothed Lines and No Data Markers. |
expression .ChartWizard(Source, Gallery, Format, PlotBy, CategoryLabels, SeriesLabels, HasLegend, Title, CategoryTitle, ValueTitle, ExtraTitle)
expression A variable that represents a Chart object.
Parameters
| Name | Required/Optional | Data Type | Description |
| Source | Optional | Variant | The range that contains the source data for the new chart. If this argument is omitted, Microsoft Excel edits the active chart sheet or the selected chart on the active worksheet. |
| Gallery | Optional | Variant | One of the constants of XlChartType specifying the chart type. |
| Format | Optional | Variant | The option number for the built-in autoformats. Can be a number from 1 through 10, depending on the gallery type. If this argument is omitted, Microsoft Excel chooses a default value based on the gallery type and data source. |
| PlotBy | Optional | Variant | Specifies whether the data for each series is in rows or columns. Can be one of the following XlRowCol constants: xlRows or xlColumns. Values can be [1 or 2] |
| CategoryLabels | Optional | Variant | An integer specifying the number of rows or columns within the source range that contain category labels. Legal values are from 0 (zero) through one less than the maximum number of the corresponding categories or series. |
| SeriesLabels | Optional | Variant | An integer specifying the number of rows or columns within the source range that contain series labels. Legal values are from 0 (zero) through one less than the maximum number of the corresponding categories or series. |
| HasLegend | Optional | Variant | True to include a legend. |
| Title | Optional | Variant | The chart title text. |
| CategoryTitle | Optional | Variant | The category axis title text. |
| ValueTitle | Optional | Variant | The value axis title text. |
| ExtraTitle | Optional | Variant | The series axis title for 3-D charts or the second value axis title for 2-D charts. |
Remarks
If Source is omitted and either the selection isn't an embedded chart on the active worksheet or the active sheet isn't an existing chart, this method fails and an error occurs.
You can use other values from above table to create graph of your choice.
[…] Via Ashwini Tripathi […]
ReplyDelete