To configure SQL Authentication on Microsoft NAV Server Instance using Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2016 Administration Shell
- If you are modifying an existing Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, run the Set-NAVServerConfiguration cmdlet.
Syntax & Parameter explaination:Set-NAVServerConfiguration (cmdlet)
-KeyName <String>
(The configuration key name. Examine the CustomSettings.config file to determine the correct key name.)
[-Element <String> ]
(Specifies the navigation path from the root element to the appSettings section of the configuration document.)
[-ServerInstance] <String>
(Specifies the name of a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance. The default instance name is DynamicsNAV90. You can specify either the full name of an instance such as MicrosoftDynamicsNavServer$myinstance or the short name such as myinstance.)
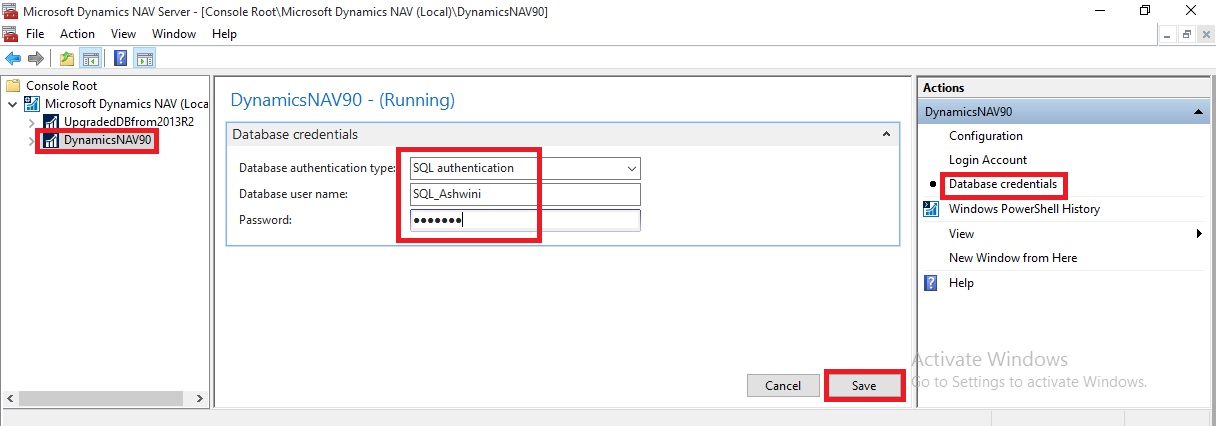
-DatabaseCredentials <PSCredential>
(The user name and password of the login account that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will use to connect to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database in SQL Server. This parameter configures the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to use SQL Server Authentication instead of Windows Authentication on the connection to the database. The login account must be a member of the
db_owner role on the database.)
[-Force] (Forces the command to run without asking for user confirmation.)
[-KeyValue <String> ] (The configuration key value.)
[-Confirm] (Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.)
[-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
Use the
DatabaseCredentials parameter to provide the login credentials of the database user that you want to use to access the application database.
Example:C:\PS>Set-NAVServerConfiguration MyInstance -KeyName DatabaseServer -KeyValue DatabaseServer.Domain.Com
- If you are creating a new Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, run the New-NAVServerInstance cmdlet.
Syntax & Parameter explaination:New-NAVServerInstance
[-ServerInstance] <String>
(Specifies the name of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance. The default instance name isDynamicsNAV90. You can specify either the full name of an instance, such as MicrosoftDynamicsNavServer$DynamicsNAV90, or the short name, such as DynamicsNAV90. You must use single-quotes around the instance name.)
-ManagementServicesPort <ServicePort>
(Specifies the TCP port that is used to manage the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance. The Management Services port has no exceptions in the firewall, and will only be accessed from the local computer. The port is used by Windows PowerShell for access Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server management data.)
[-ClientServicesCredentialType <String> ]
(The type of client credential used for client authentication.Possible values are: Windows, Username, NavUserPassword and AccessControlService.)
[-ClientServicesPort <ServicePort> ]
(Specifies the listening TCP port for clients such as Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client.)
[-DatabaseCredentials <PSCredential> ]
(The user name and password of the login account that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will use to connect to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database in SQL Server. This parameter configures the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to use SQL Server Authentication instead of Windows Authentication on the connection to the database. If the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance is configured for multitenancy, then parameter configure SQL Authentication on the connection to the application database, not the tenant database. The login account must be a member of the db_owner role on the database.)
[-DatabaseInstance <DatabaseInstance> ]
(Specifies the SQL Server instance on which the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database is installed.)
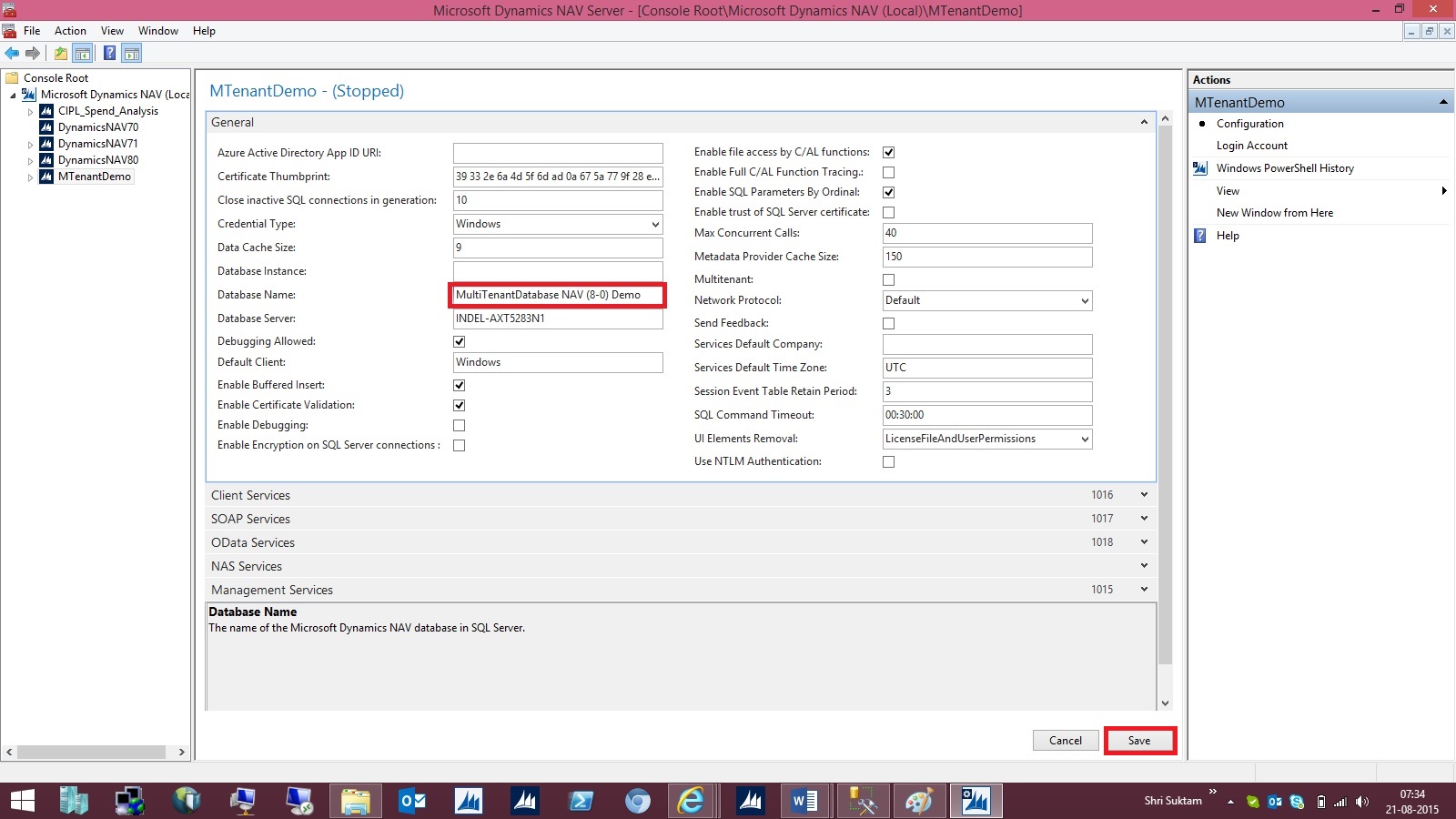
[-DatabaseName <DatabaseName> ]
(Specifies the name of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database.)
[-DatabaseServer <DatabaseServer> ]
(Specifies the name of the computer on which the SQL Server instance for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database is installed.)
[-Force] (Forces the command to run without asking for user confirmation.)
[-Multitenant]
(Specifies the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to be a multitenant instance.)
[-ODataServicesPort <ServicePort> ]
(Specifies the listening HTTP port for Microsoft Dynamics NAV OData web services.)
[-ServiceAccount <ServiceAccount> ]
(Specifies the Windows-based computer account that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance must use to log on. The default value is NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE. Only NetworkService and User values are supported. This parameter accepts values from the enum System.ServiceProcess.ServiceAccount.)
[-ServiceAccountCredential <PSCredential> ]
(Specifies a set of security credentials that you must use when configuring the service account.)
[-ServicesCertificateThumbprint <ClientServicesCertificateThumbprint> ]
(Specifies the certificate thumbprint for the x509 certificate that is going to be used for securing communication with the server. The certificate must be stored in the local machine store and in the personal sub-store in the certificate store. The private key of the certificate must be present and exchangeable. The certificate must be in .pfx format, not .cer format. The certificate can be either self-signed or issued by a trusted certification authority (CA).
When specifying a ServicesCertificateThumbprint, SOAP web services and OData web services become HTTPS.)
[-SOAPServicesPort <ServicePort> ]
(Specifies the listening HTTP port for Microsoft Dynamics NAV SOAP web services.)
[-Confirm] (Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.)
[-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
Use the
DatabaseCredentials parameter to provide the login credentials of the database user that you want to use to access the application database.
Examples:C:\PS>New-NAVServerInstance NewInstance -ManagementServicesPort 8099 -ClientServicesPort 8100 -SOAPServicesPort 8101 -ODataServicesPort 8102 –verbose
C:\PS>Get-Credential | New-NAVServerInstance NewInstance -ServiceAccount User -ManagementServicesPort 8099 -ClientServicesPort 8100 -SOAPServicesPort 8101 -ODataServicesPort 8102 –verbose
For Multitenant Environment
- Configure SQL Server Authentication with the application database as above.
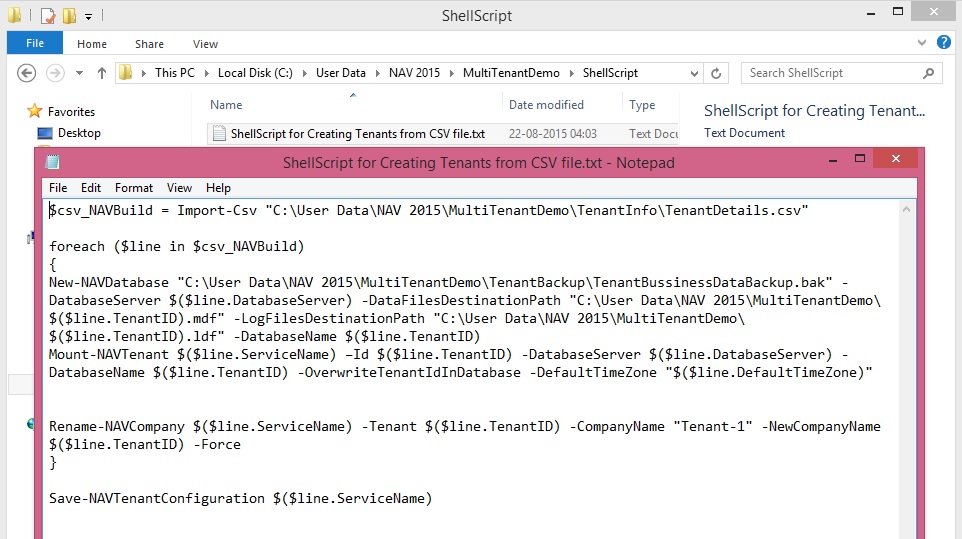
- To configure SQL Authentication with the tenant database, run the Mount-NAVTenant
Syntax & Parameter explaination:Mount-NAVTenant
[-AlternateId] <System.Collections.ObjectModel.ReadOnlyCollection[string]>
(Specifies the alternative IDs for the tenant, such as host names for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client, SOAP web services, OData web services, or the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
If you use alternative IDs for tenant resolution in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client, you must also enable some of the UrlRewrite rules in the Web.Config file for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components.)
[-AzureKeyVaultSettings] <Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Types.AzureKeyVaultSettings>
(Specifies the Azure key vault settings. This parameter is available only if the
EncryptionProvider is set to
AzureKeyVault.)
[-ServerInstance] <String>
(Specifies the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that you want to mount the tenant against, such as DynamicsNAV90. You can specify either the fully qualified name, such as 'MyServer$DynamicsNAV90', or the short name, such as 'DynamicsNAV90'.)
[-DatabaseInstance] <System.String>
(Specifies the name of the SQL Server instance that hosts the database. You can also specify the instance in the
DatabaseServer parameter, such as
MyServer\MyInstance.)
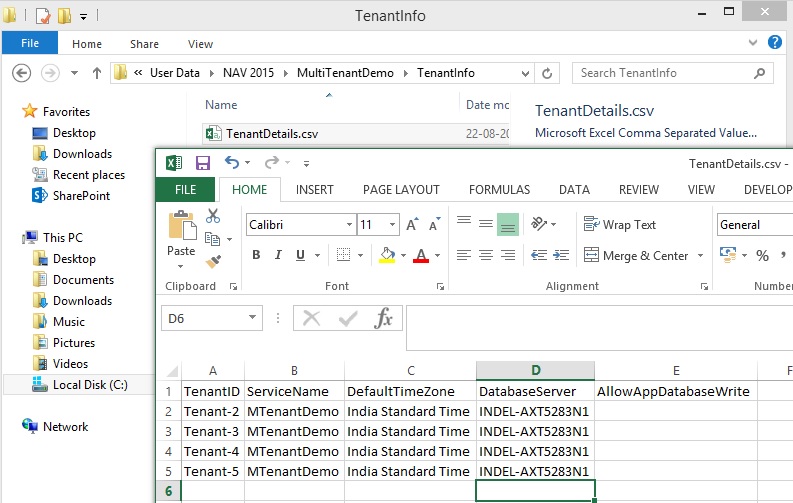
[-DatabaseName] <System.String>
(Specifies the name of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database that you want to mount against the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, such as 'Demo Database NAV (9-0)'.)
[-DatabaseServer] <System.String>
(Specifies the name of the database server that hosts the Microsoft Dynamics NAV database that you want to mount against the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.)
[-DefaultCompany] <System.String>
(Specifies the name of the company that NAS services, OData web services, and SOAP web services use if no other company is specified.)
[-DefaultTimeZone] <System.TimeZoneInfo>
(Specifies the default time zone that is used by the NAS services, OData web services, and SOAP web services for this tenant.
You can set the parameter to UTC, 'Server Time Zone', or the ID of a Windows Time Zone.
UTC specifies that all business logic for services on the server instance runs in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
'Server Time Zone' specifies that services use the time zone of the computer that is running Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.
ID of a Windows Time Zone specifies that services use a Windows time zone as defined in the system registry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Time Zones. For example, Romance Standard Time is a valid Windows time zone value.
If this parameter is not specified, the value is taken from the ServicesDefaultTimeZone setting in the CustomSetting.config file for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.)
[-NasServicesEnabled]
(Specifies to enable NAS services on the tenant. The default value is
false.)
[-RunNasWithAdminRights]
(Specifies the NAS services to run with administrator rights. This grants the NAS service the same permissions as the SUPER permission set in Microsoft Dynamics NAV without having to add the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server service account as a user. The default is
false.)
[[-ApplicationDatabaseCredentials] <PSCredential> ]
(Specifies the user name and password of the login account that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will use to access the application database in SQL Server. This parameter configures the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to use SQL Server Authentication instead of Windows Authentication on the connection to the application database.
The login account must be a member of the db_owner role on the database.
This parameter is only relevant when you set with the ApplicationDatabaseServer and ApplicationDatabaseName parameters )
[[-ApplicationDatabaseName] <System.String> ]
(Specifies the name of the application database to use with the tenant database.
This parameter is only relevant if the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance is configured for multitenancy. This parameter, together with the ApplicationDatabaseServer parameter, enables you to mount a tenant to the same Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance as the application database without having to connect a running Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.)
[[-ApplicationDatabaseServer] <System.String> ]
(Specifies the SQL Server name and instance, such as MyServer\MyInstance, that hosts the application database that you want to use with the tenant database,.
This parameter, together with the ApplicationDatabaseName parameter, enables you to mount a tenant to the same Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance as the application database without having to connect to a running Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance.)
[-AllowAppDatabaseWrite]
(Specifies if the tenant can write to the application database. The default value is
false.)
[-DatabaseCredentials <PSCredential> ]
(Specifies the user name and password of the login account that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance will use to access the tenant database in SQL Server. This parameter configures the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance to use SQL Server Authentication instead of Windows Authentication on the connection to the database.
The login account must be a member of the db_owner role on the database.)
[-EncryptionProvider <Microsoft.Dynamics.Nav.Types.EncryptionProvider> ]
(Specifies the name of the encryption provider.)
[-Force] (Forces the command to run without asking for user confirmation.)
[-OverwriteTenantIdInDatabase]
(Specifies if the Mount-NAVTenant cmdlet must overwrite the tenant ID in the database if the database has been mounted as a tenant earlier. If this is
false, and the tenant database has previously been mounted with a different tenant ID, an exception is thrown.)
[-Confirm] (Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.)
[-WhatIf] [ <CommonParameters>]
Use the
DatabaseCredentials parameter to provide the login credentials of the database user that you want to use to access the tenant database.
Examples:PS C:\> Mount-NAVTenant DynamicsNAV90 -Id 'Test' -DatabaseName 'Test_Database'
PS C:\> Mount-NAVTenant DynamicsNAV90 Test Test_Database
PS C:\> Mount-NAVTenant DynamicsNAV90 -Id 'Test' -DatabaseName 'Test_Database' -DatabaseCredentials (Get-Credential)
PS C:\> Get-NAVTenant Server1 | Mount-NAVTenant Server2
PS C:\> Get-NAVTenant Server1 | Dismount-NavTenant Server1 -Force | Mount-NAVTenant Server2
PS C:\> Mount-NAVTenant DynamicsNAV90 -Id 'Test' -DatabaseName 'Test_Database'-AlternateId @( "test.mydomain.com", "http://mydomain.sharepoint.com/sites/teamsite" )
PS C:\> Mount-NAVTenant -Id 'Test' -DatabaseName 'Test_Database' -DatabaseCredentials (Get-Credential) -ApplicationDatabaseServer 'MySQLServer\NAV' -ApplicationDatabaseName 'MyNavAppDatabase' -ApplicationDatabaseCredentials (Get-Credential) -KeyFilePath 'C:\key\nav.key' -KeyFilePassword (Get-Credential).Password